Background: Allogeneic transplantation (allo-HCT) is a potentially curative treatment for a variety of hematologic malignancies and nonmalignant hematologic disorders. Allo-HCT from a haploidentical (Haplo) related donor has emerged as a suitable alternative in the absence of matched related donor (MRD) and matched unrelated donor (MUD). Haplo HCT patients however have higher risk of graft rejection and graft versus-host disease (GVHD). Thus, patients often receive post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy), which has proven to be highly effective in reducing GVHD. While the use of peripheral blood is an attractive option due to the ease of collection and rapid peripheral blood count recovery, not much information is available on the impact of graft sources using PTCy in Haplo-HCT. This study compares outcomes of bone marrow (BM) versus peripheral blood (PB) stem cell graft for Haplo-HCT in adult patients.
Methods: We performed a retrospective study of 81 adult patients who underwent Haplo-HCT at The Ohio State University from 2009 to 2018. The study endpoints were overall survival (OS), progression free survival (PFS), non-relapse mortality (NRM), relapse, engraftment, acute GVHD (grade II-IV), and chronic GVHD. All endpoints were measured from the time of transplantation. Patient, disease, and transplant-related characteristics were compared between the two groups (BM versus PB) using the Mann-Whitney U test for continuous variables, and chi-squared or Fisher's exact test for categorical variables. The probabilities of OS and PFS were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier (KM) method and compared using log-rank test. Cumulative incidence rates were estimated and compared using Gray's test accounting for competing risks.
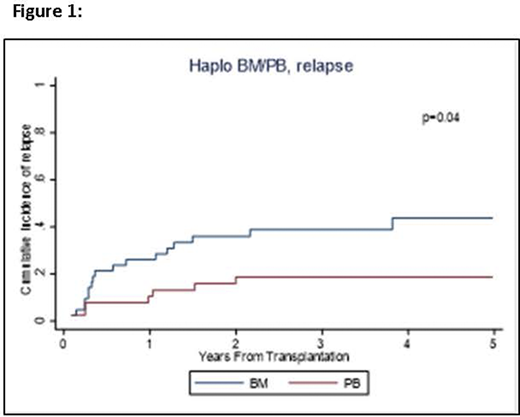
Results: We compared the outcomes of patients who received a BM graft (N=43) with those receiving a PB graft (N=38). The median age at transplant was 57 years (20-74). All patients received PTCy in addition to tacrolimus and mycophenolate in 91% of patients. Reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) was used in majority of patients (N=63, 78%). The two groups were comparable including age (median, 60 years for BM and 56 years for PB, p=0.60) and the type of conditioning regimen (79% RIC for BM, 76% RIC for PB, p=0.77). The number of CD34+ and CD3+ infused cells was higher in PB grafts (median, 8.6x106 CD34+ cells/Kg, 2.0 x108 CD3+ cells/Kg, respectively) than for BM (median, 3.7x106 CD34+cells/Kg, 0.4x108 CD3+cells/Kg, respectively). Time to neutrophil and platelet engraftment were significantly shorter in patients receiving PB versus those getting BM grafts: median 15 vs. 17.5 days, (p=0.02) and median 20 vs. 29 days (p<0.01) respectively. In univariable analysis there was no difference in OS (p=0.30), PFS (p=0.29) or NRM (p=0.33) between the groups. The BM cohort showed a 3-year OS rate of 62% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 45-75), and 3-year PFS of 48% (95% CI: 32-62). For PB group, 3-year OS and PFS were 68% (95% CI: 50-80) and 60% (95% CI: 43-74), respectively. There were no differences in the incidence of acute GVHD (p=0.80) and chronic GVHD (p=0.53). For BM vs. PB, cumulative incidences of grade II-IV acute GVHD at day +180 were 57% (95% CI: 41-70) vs. 55% (95% CI: 69-38) and for chronic GVHD at day 365, they were 40% (95% CI 26-55) vs. 47% (95% CI: 31-62), respectively. There was a significant difference in the incidence of relapse (p=0.04, Figure 1) with 2-year relapse rate of 36% (95% CI: 22-50) for BM vs. 19% (95% CI: 8-32) for PB. After controlling for conditioning regimen, PB graft had a reduced risk of relapse compared to BM graft, HR=0.35 (95% CI: 0.13-0.93, p=0.03).
Conclusion: Our study suggests peripheral blood for haploidentical transplant to be a good alternative to bone marrow. Similar PFS, OS and NRM were seen between the two graft sources. As expected, faster neutrophil and platelets engraftment were seen with PB due to more CD3+ and CD34+ infused, but without an increase in acute or chronic GVHD. A reduced relapse risk was observed with PB graft. Our study is small and is retrospective, but provide encouraging results. A prospective randomized controlled trial is required to confirm these results.
Chaudhry:Sanofi: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Bumma:Sanofi: Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Speakers Bureau. Khan:Amgen: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy. Devarakonda:Janssen: Consultancy. Vasu:Kiadis Inc: Other: Kiadis has obtained exclusive licensing requirements from The OHio State University; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Omeros: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Jaglowski:Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Juno: Consultancy; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; CRISPR: Consultancy. William:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Dova: Research Funding; Kyowa Kirin: Consultancy, Honoraria; Guidepoint Global: Consultancy; Incyte: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria. Mims:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Other: Data Safety Monitoring Board; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Syndax Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kura Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Leukemia and Lymphoma Society: Other: Senior Medical Director for Beat AML Study; Agios: Consultancy; Novartis: Speakers Bureau. Brammer:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Kymera: Honoraria; Verastem Oncology: Other: Travel. Saad:Amgen: Other: research support; Magenta Therapeutics: Other: Personal Fees; Incyte Pharmaceuticals: Other: Personal Fees; Orcabio: Other: research support; Kadmon: Other: research support. Efebera:Celgene: Research Funding; Ohio State University: Current Employment; Takeda: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal